Key Issues and Common Solutions for Cryogenic Pumps
Key Issues and Common Solutions for Cryogenic Pumps
Cryogenic pumps are critical components in LNG and other low-temperature applications. Understanding their design, common issues, and troubleshooting methods is crucial for maintaining efficient and reliable operations.
Introduction to Cryogenic Pumps
Cryogenic pumps have greatly evolved since their emergence in the mid-twentieth century, becoming highly reliable and efficient. They fall into two categories:
- Submerged Motor Pumps (SMP)
- External motor pumps with air-cooled systems
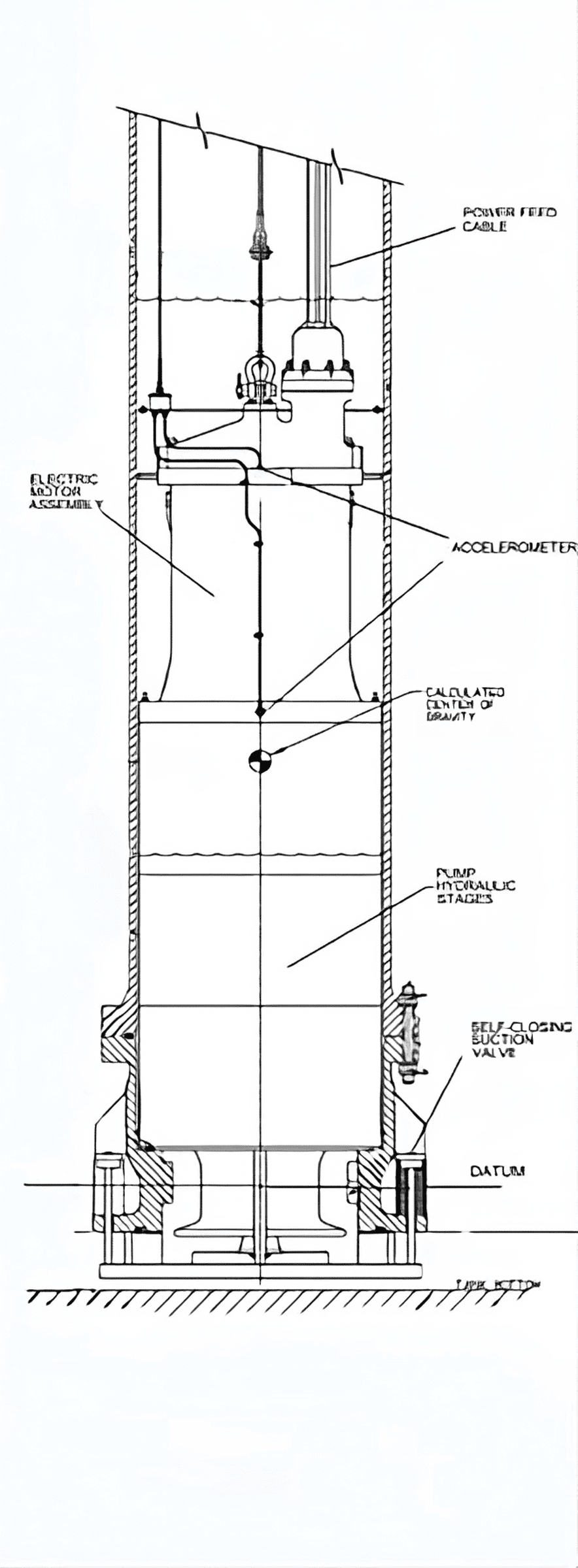
For LNG applications, SMPs are predominantly used. The submerged pump and motor assembly is located in the tank, cooled and lubricated by the cryogenic liquid. This design provides a highly reliable and robust compact solution due to the short shaft length and low NPSHr, avoiding seal issues as there are no mechanical seals in the submerged solution.
Design and Operation
- Pumps have single or multi-stage hydraulics specifically designed for the application.
- Common pumped liquids include LNG, LPG, liquid ethylene, and various others.
- Reliable long-term operation depends on balancing axial loads on rotor support bearings, often using a Thrust Equalising Mechanism (TEM).
- High-performance inducers reduce NPSHr and allow for low-level drawdown of the tank.
- Materials of construction are specifically selected for their mechanical and thermal properties at cryogenic temperatures.

Common Issues
- Seal Failures: In external motor cryogenic pumps due to extreme temperatures and pressure variations.
- Shaft Breakages: Caused by excessive vibration levels and fatigue at localized high stress points.
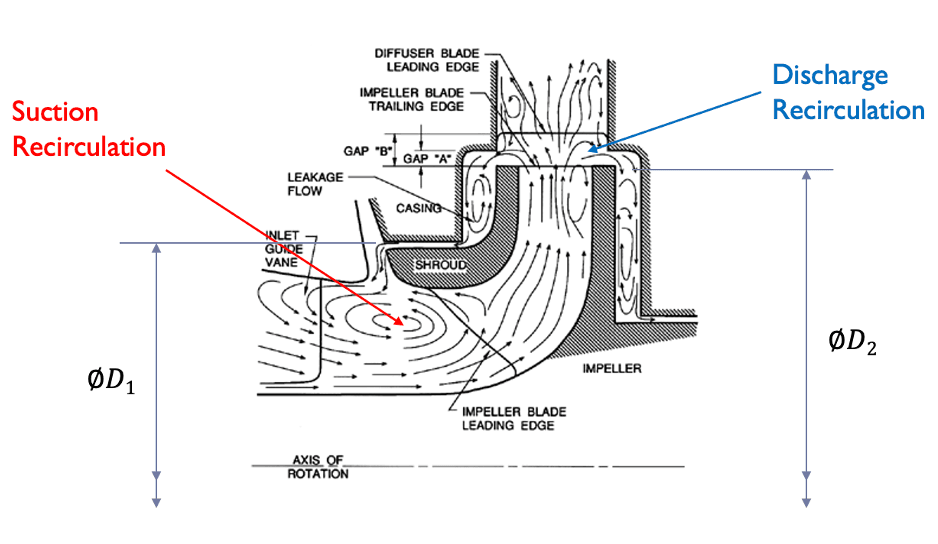
- Cavitation: Occurs when the cryogenic liquid vaporizes due to heat or low pressure.
- Vibration and Noise: Can lead to mechanical failures and operational inefficiencies.
- Maintenance Challenges: Due to the specialized nature of cryogenic pumps.
Troubleshooting and Analysis
Troubleshooting should be carried out methodically, starting with a system audit:
- Verify pump construction, rating, and system design meet current operational requirements.
- Analyze vibration signatures for early failure prediction.
- Conduct rotordynamic stability analysis when necessary.
- Perform bump tests of the support structure to check for resonance.
- Use both experimental and analytical approaches to resolve issues.

Common Solutions
- Improved Seal Designs: Using advanced materials for external motor pumps.
- Cavitation Prevention: Maintaining adequate suction pressure and using anti-cavitation devices.
- Material Selection: Choosing materials that withstand extreme cryogenic conditions.
- Vibration Control: Employing tighter dynamic balancing, stiffening, and vibration dampening.
- Regular Maintenance: Establishing robust maintenance schedules and personnel training.
Why This Matters
Efficient operation of cryogenic pumps is crucial for:
- Ensuring safety in handling extremely low-temperature liquids
- Maintaining the integrity of LNG and other cryogenic processes
- Reducing downtime and operational costs in critical industrial applications
- Meeting stringent regulatory requirements in the LNG industry
Did You Know?
- Cryogenic pumps can operate at temperatures as low as -196°C (-320°F).
- The cool-down of a submerged pump is a critical operation due to varying thermal behaviors of components.
- Cryogenic pumps have an expected design life exceeding 20 years.
Further Reading
For more in-depth information on cryogenic pumps and their applications:
- Cryogenic Society of America - Cryogenic Pump Basics
- International Cryogenic Engineering Conference Proceedings
Authors
David Cullen – Cryogenic Systems Expert Jean-Noel Bajeet – Machinery Consultant
Contact
For more information and support, please contact:
Dr Jean-Noel Bajeet FIMechE CEng
Lead Consultant
Jean-noel.bajeet@fluensys.co.uk
While every effort has been made to provide a comprehensive overview of best practices in resolving issues with cryogenic pumps, Fluensys does not claim that these will successfully apply to every system and may require a more in-depth analysis to form a valid technical opinion based on the specifics of the application.
Download Full Article
Get a PDF version of this article for offline reading and sharing.
Related Articles in [ troubleshooting ]
Subscribe to Our Blog
Stay updated with our latest articles and insights.